TL;DR
- SPF = what IPs and domains are allowed to send emails for your domain
- DKIM = digital signature to ensure email is not tampered with
- DMARC = tells email servers how important SPF and DKIM are, and what to do when an email fails to pass their tests (incl. where to send email reports to)
OVERVIEW & SETUP PROCESS
10 Oct 2024
SPF, DKIM & DMARC are TXT records to add to the domain's DNS.
SPF: Sender Policy Framework - identifies the mail servers that are allowed to send messages for your domain.
DKIM: Domain Keys Identified Mail - email authentication method designed to detect forged sender addresses in emails (email spoofing).
DKIM works by adding a digital signature to the headers of your outgoing email messages. This signature is created using a private key that only your domain’s mail server has access to. The recipient’s mail server can then use the public key (published as a DNS TXT record) to verify that the email was sent from an authorized source and that it hasn’t been tampered with in transit.
DMARC: Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance - tells email servers how important SPF and DKIM are, and what to do when an email fails to pass their tests.
Process:
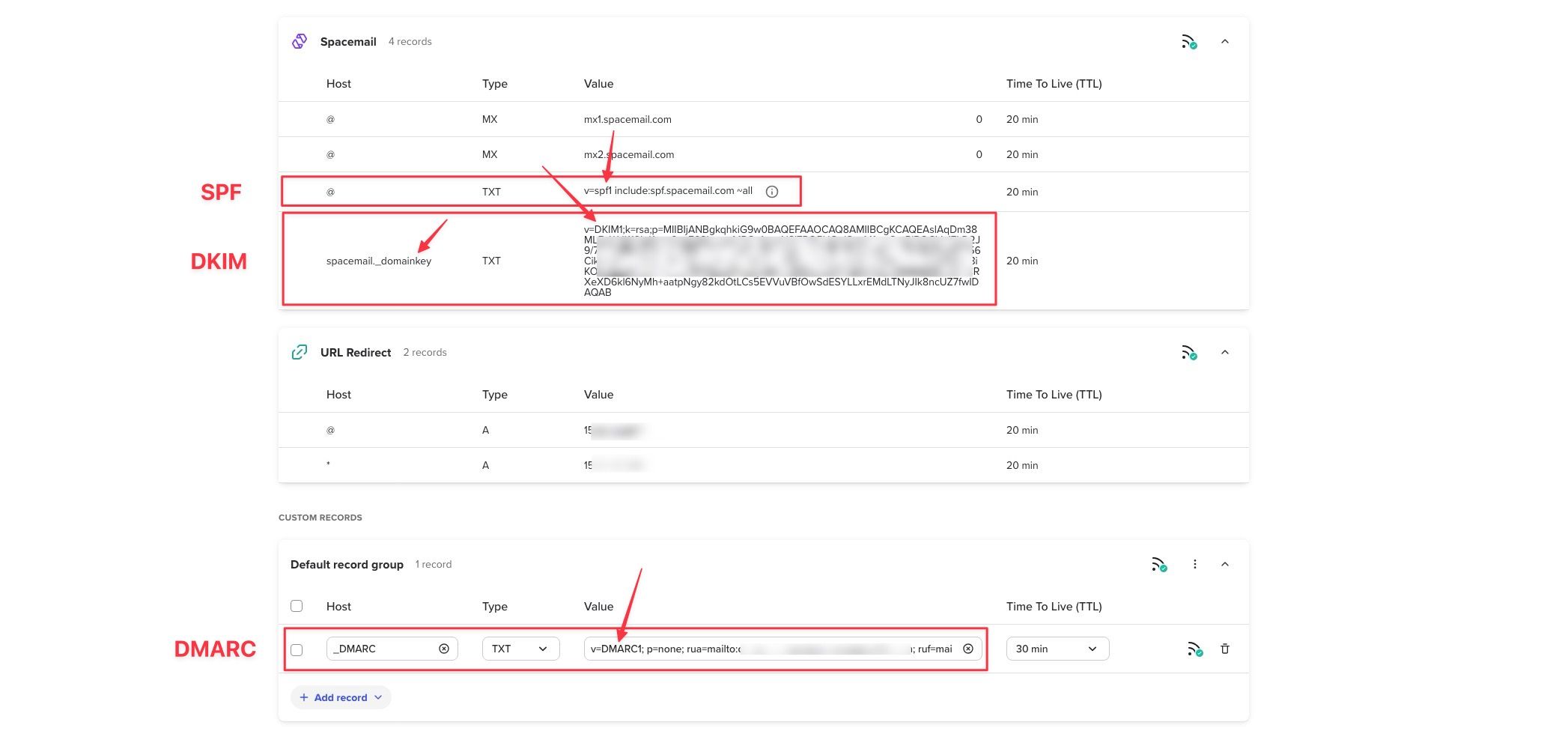
- create the DNS records for SPF, DKIM & DMARC at domain level from which emails are sent. They should look like this:
SPF
Type: TXT
Host: @
Value: v=spf1 include:_spf-eu.ionos.com ~all
This would be the value to start with, using your default email provider's value for include:.
See below for how to use DMARC to get reports on what is happening with your emails & update the SPF record with the IPs of the email sending services you are actually using (eg email automation platforms).
DKIM
Type: TXT
Host: spacemail._domainkey
Value: "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKOz56wSqPQIDAQAB"
How to generate the value for DKIM: use a DKIM record generator tool, like the one from EasyDMARC or DMARCLY (see below).
DMARC
Type: TXT
Host: _dmarc
Value: v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:{email_to_receive_reports}; ruf=mailto:{email_to_receive_reports}; fo=1
p can be none, quarantine or reject.
rua and ruf are the email addresses where you want to receive the reports.
fo is the percentage of emails that should be checked by the receiving server. 1 means 100%.
- the DMAC record should be set to
p=noneto start with (possibly later top=quarantineand finallyp=rejectonce everything is working fine) - from the zipped XML records that are received to the email address indicated in the DMARC record, you can see what is going on with your emails, ie what IPs are sending emails (eg Instantly or Smartlead)
- update the SPF record with the IPs of the email sending services you are using, so they are allowed to send emails on your behalf, for example (scrambled IPs for the example):
v=spf1 ip4:209.85.220.41 ip4:212.227.126.134 ip4:82.165.159.38 ip4:217.72.192.74 ip4:212.227.17.10 ip4:52.165.46.30 ip4:212.227.17.24 ip4:217.72.192.73 ip4:212.227.17.13 ip4:212.227.126.131 ip6:2a01:111:f403:2608::707 include:_spf-eu.ionos.com ~all
In this updated record you can see all the IPs used by the email sending services you are using, and the include: value from the default email provider.
Here is how those records look like in the DNS settings of the domain provider:
Then in your email automation platform:
Ensure you indicate the SPF, DMARD & DKIM selector (eg google) and the domain (eg mydomain.com) in the email settings.
Then, when sending emails, ensure you are sending from the domain that has the SPF, DKIM & DMARC records setup.
Check the DMARC reports for a while to ensure no issues with email delivery, and update the SPF record accordingly (ie with new IPs of email sending services you are using).
IMPORTANT: in Smartlead, DNS verification only requires the unique part of the selector, eg
spacemailand notspacemail._domainkeyto pass validation.
If you set your DMARC policy to “quarantine”, the following will occur when an email fails DMARC validation:
1. Emails Will Be Sent to Spam/Junk Folder:
Emails that fail the DMARC checks (i.e., those that do not align with either SPF or DKIM) will be directed to the recipient’s spam or junk folder instead of their inbox.
2. Visibility to Email Recipients:
While the email won’t be outright rejected, it will be flagged as suspicious, leading to reduced visibility, as most users don’t check their spam folder regularly.
3. Reporting:
The recipients’ email servers will still send you reports about these failed emails. You’ll get aggregate reports on DMARC failures (if you’ve set up a reporting mechanism), which helps you track the effectiveness of your policy and identify problematic emails.
4. Recipient Action:
Some recipients may manually mark the email as “Not Junk” or “Not Spam”, which can help in improving future deliverability if done by enough people.
5. Effect on Brand and Deliverability:
Setting the DMARC policy to “quarantine” is a step toward stricter email authentication. While it increases security, it could initially lead to legitimate emails being sent to spam if SPF/DKIM is not properly aligned, so you should ensure that your SPF, DKIM, and email sending practices are in good order before applying this policy. Over time, it can improve your domain’s reputation by blocking or isolating potentially malicious or spoofed emails.
In summary, using “quarantine” helps to protect your domain by marking potentially fraudulent emails as suspicious, but it requires well-configured email authentication (SPF, DKIM) to prevent your legitimate emails from landing in spam.
NOTES
05 Dec 2022
When using your own domain, by default, emails are not setup to be delivered properly.
Emails might be sent, but they might not be delivered, ie they might get caught in spam filters more often than not.
Some technical setup is required, to ensure receiving server will see your emails as trustworthy.
If you know your way with DNS records, it's fairly easy to setup yourself once you wrap your head around what SPF, DMARC, etc.. are.
Else, this can be all a bit technical - I recommend using a gig/service (see "Done for you" section below).
Overview

Check
You can start first by doing a Spam check with:
This provides results like: https://spamchecker.mailreach.co/tests/1d0bc68bfeb8

Then use tools to check your current setup.
Use tools like EasyDMARC:

or PowerDMARC:

or MXtoolbox:

or Sender Score (GATED):

➤ not great, just basic checks
Blocklist check (also GATED):

Domain Setup
At domain level, specific DNS records need to be setup to ensure that emails are delivered properly.
Bare minimum are MX records
Though these just ensure that emails can be received, but does not guarantee sent emails will be delivered.
To ensure deliverability, you need to setup the following:
Critical:
Good to have:
Optional & new (but costly):
- BIMI (optional - if you want to display your logo in the inbox + added deliverability)
Optional if using email tools with tracking:
- Custom Tracking Domain (optional - if email tracking is important to you)
DNS Records
Basically, this means adding DNS records like these to your domain name:
SPF
Just a DNS text record along the lines of TXT @ v=spf1 include:_spf-eu.ionos.com ~all - just need to find from provider what to put in as include: value.
Sender Policy Framework identifies the mail servers that are allowed to send messages for your domain.
DMARC
Just a DNS text record along the lines of TXT _dmarc v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:XXXX@XXXX.XXXX; pct=90; sp=none.
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance

Generate your DMARC record with this tool:

then add DNS record, eg:
v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:email-example@btobsales.eu; pct=90; sp=none as TXT file named _dmarc.btobsales.eu.

SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are complementary systems. SPF and DKIM are used by email servers as indicators of whether or not an email is spam. DMARC then does two things: it tells email servers how important SPF and DKIM are, and what to do when an email fails to pass their tests.
Custom Tracking
If you use a custom tracking domain, DNS record along the lines of:
CNAME inst prox.itrackly.com
This will be provided by your email tracking provider.
DKIM
DNS record along the line of TXT google._domainkey.mydomain.com "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GN[....]ADCBiQKOz56wSqPQIDAQAB" with a public key.
Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method designed to detect forged sender addresses in emails (email spoofing), a technique often used in phishing and email spam.
Basically, content of email gets hashed and added to header with server signature.
When receiving server gets email, it can check with sending server if signature is valid.
Good article about it from IONOS:
https://www.ionos.com/digitalguide/e-mail/e-mail-security/dkim-domainkeys/
DKIM Record Generator:

DKIM Record Generator
Use this DKIM Record Generator to create your DKIM record:

DKIM Record Checker

BIMI
Optional
BIMI is a new standard that allows you to display your logo in the inbox. It also helps with deliverability as it's built on top of DMARC and requires a 3rd party to validate your logo.

You need to make sure that your logo is registered and recognized as an official trademark. VMC certificates will not be granted to any brand logos that aren’t registered by an official intellectual property office.
It's expensive though, eg with Entrust:
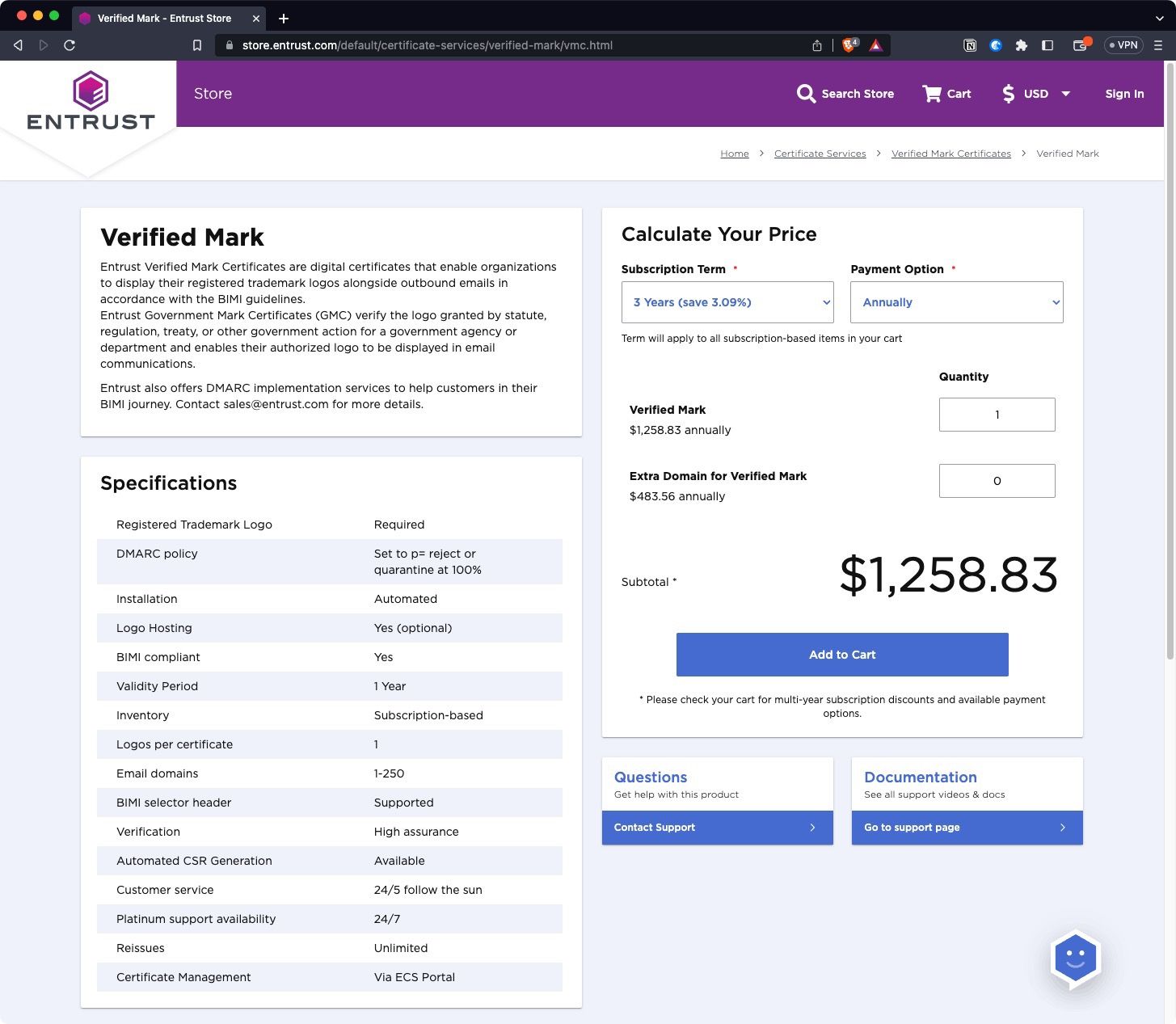
https://store.entrust.com/default/certificate-services/verified-mark/vmc.html
or Digicert:
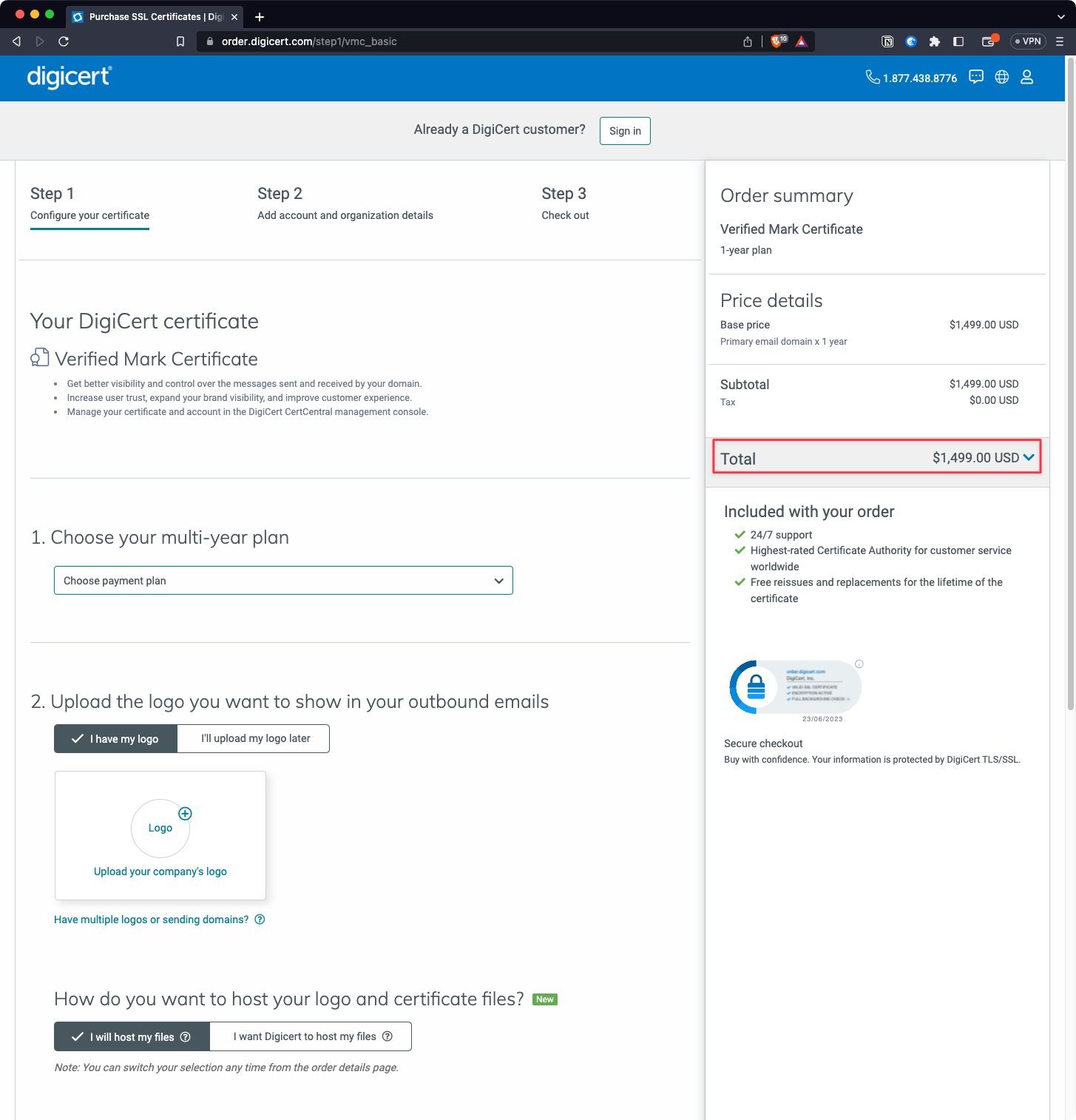
https://order.digicert.com/step1/vmc_basic
Check your IP reputation


Deliverability services
EasyDMARC

from 40EUR/month!
PowerDMARC

starts at $8/month
DMARCly

starts at $18/month
Deliverability diagnostics
Email headers check
Check email headers with this tool:

Spam blacklist check

Allegrow

$70 per mailbox per month
Folderly

➤ $200/month!
Free check from Google Admin:

DMARC reports

Email Warming
Lemwarm
To warm up an email, you can use:

Instantly.ai
04 Jun 2023 started testing to replace Lemwarm. Much cheaper to run multiple emails/accounts, and looks as good if not better.

Mailreach
$25/email account/month (!!!)
Inboxy

Tool built by https://www.leadbird.io/
Done For You
In the past, before diving in the topic myself, I used a Fiverr gig to get my email setup properly.
Plenty of gigs for this type of task:

04 Jun 2023 came across Leadhype, referred by Instantly.ai. Looks like a good option to outsource the whole process.

Verify Emails
See Tools for email finding & validation#email-verification
Email content
To maximise deliverability when engaging a new domain for the first time:
- no HTML
- no files
- no images / at least not in the first email(s) with a given domain recipient)
- links in plain text
14 Jul 2023
While not directly impacting deliverability, I learned that event sending links as plain text get caught by link protection systems (eg https://link.edgepilot.com from Appriver - so a link like https://dryfta.com appears as https://link.edgepilot.com/s/7b020da3/9N9is50NekuEJT0J1a8VRQ?u=https://dryfta.com/).
This means links don't land straight on the given page, but rather on some sort of proxy sandbox page I believe.
Not sure about the user experience.
Email volume
To not impact your reputation, send max 100 emails/day. Start at 10/day.
Optimise for answers
Even if it's a "no", at least you can disqualify the email, while not impacting your reputation.
A/B test your sequences.
Resources
29 Sep 2024
Smartlead Email Deliverability Guide
Carlos Fenollosa - Blog
22 Apr 2025

The article discusses how email deliverability is being deliberately nerfed by Big Tech companies, making it difficult for small email servers to reach their recipients. The author argues that this is an anti-competitive practice, using spam as a scapegoat to stifle competition and force others to use their email sending APIs.
Here are the main points:
- Email deliverability is deliberately nerfed: Big Tech companies like Google and Microsoft are using blacklisting protocols to block emails from small servers, making it difficult for them to reach their recipients.
- Spam is used as a scapegoat: The author believes that spam is being used as an excuse to justify the blocking of emails from small servers, rather than implementing more effective anti-spam measures.
- Anti-competitive practices: The author argues that this practice is anti-competitive, as it forces others to use Big Tech's email sending APIs, which can be expensive and restrictive.
- Proposed solution: The author proposes a simple solution, which includes:
- Keeping anti-spam measures in place
- Changing blacklisting protocols to use an exponential cooldown penalty instead of permanent bans
- Allowing recourse for legitimate servers to prove their legitimacy
- Stopping blackholing (blocking emails without notification)
- Regulation is coming: The author warns that if the industry does not self-regulate, politicians may step in and impose regulations, which could be worse for everyone.
- Email interoperability is important: The author highlights the importance of email interoperability, citing the fact that email usage is higher than social networking, and that institutions like governments rely on email for secure communication.
Overall, the article argues that Big Tech companies are abusing their power to stifle competition in the email industry, and that this practice needs to be addressed through self-regulation or government intervention.
